r vs k selection|Difference between r and K Selection : Baguio R/K selection theory is a way of describing the "quality vs. quantity" reproduction strategies we see in nature. R-strategy organisms produce a ton of babies but don't spend a lot of energy . See if You’re a Lotto Texas Two Step Lottery Winner. To find out if you’ve won the Two Step jackpot, compare your 4 selected numbers and Bonus Ball number (both from a field of 35) with the winning numbers drawn. If your 4 numbers and Bonus Ball match up- congratulations, you’re a Two Step jackpot winner!
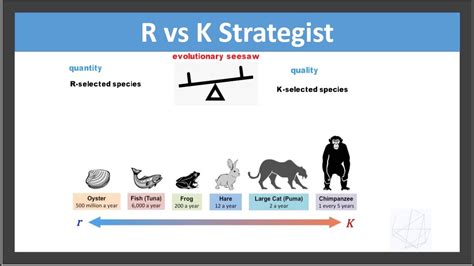
r vs k selection,Learn how r-selected and K-selected species differ in their life history strategies, traits, and population growth. See examples of r/K strategies and how to graph them.
R/K selection theory is a way of describing the "quality vs. quantity" reproduction strategies we see in nature. R-strategy organisms produce a ton of babies but don't spend a lot of energy .
r vs k selection Paul Andersen explains the differences between an r and a K selected species. He starts with a brief description of population growth noting the importance of; r or growth .K selected species sets it at risk of extinction because of the following reasons: K selected species tend to be bigger, so they need more habitat to live in. K selected species tend to have fewer offspring, so their populations cannot .Learn how biofilms exhibit both K-selection and r-selection strategies depending on environmental conditions and life cycle stages. Compare the characteristics and examples of r-selected and K-selected organisms and how biofilms .Learn how r- and K-selection theory explains the trade-offs between reproduction and survival in different organisms. Compare the characteristics and examples of r-selected and K-selected species, and how they adapt to their environments.
"K" stands for Kapazitätsgrenzen which is german for capacity limit, now called carrying capacity, K strategists have a low r and a high K. They grow slow but more survive.
Learn about the differences between r and K selected populations, which are based on the number and quality of offspring. See examples of r and K selected organisms, such as .

The theory of r - and K -selection was one of the first predictive models for life-history evolution. It helped to galvanize the empirical field of comparative life-history and .
Their reproductive strategy is to grow slowly, live close to the carrying capacity of their habitat and produce a few progeny each with a high probability of survival. Typical K-selected organisms are elephants, and humans. The table below .r vs k selection Difference between r and K Selection ing a whole subsection entitled "r and K selection". By the sixth edition, Pianka presents a multifaceted categorization of life-history traits (adapted from Winemiller 1992) with r- and K-selection as one axis of variation and "bet hedging" as another. As a con-cept, r- and K-selection appears to be a standard part
The theory of r- and K-selection was one of the first predictive models for life-history evolution. It helped to galvanize the empirical field of comparative life-history and dominated thinking on . Khanmigo is now free for all US educators! Plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our AI teaching assistant. Abstract. Increased root exudation under elevated atmospheric CO 2 and the contrasting environments in soil macro- and microaggregates could affect microbial growth strategies. We investigated the effect of elevated CO 2 on the contribution of fast- ( r-strategists) and slow-growing ( K-strategists) microorganisms in soil macro- and microaggregates.We .The terms of r- and K-selection were introduced to ecology by MacArthur and Wilson (1967), although some aspects of these concepts were considered earlier by Dobzansky (1950). When food reserves limit population size, K selection takes over, and increase in one genotype must be at the expense of another. Whereas r selection operates in ecological situations where food reserves fluctuate drastically, and species are favored that reproduce rapidly and produce large numbers of offspring.Life history theory (LHT) is an analytical framework [1] designed to study the diversity of life history strategies used by different organisms throughout the world, as well as the causes and results of the variation in their life cycles. [2] It is a theory of biological evolution that seeks to explain aspects of organisms' anatomy and behavior by reference to the way that their life . Paul Andersen explains the differences between an r and a K selected species. He starts with a brief description of population growth noting the importance . According to r/K selection theory, organisms can be categorized as r-selected or K-selected based on their life history traits that are associated with different ecological and environmental conditions. r-Selected Species. r-selected species are those that have a high reproductive rate and produce many offspring with little parental investment.Difference between r and K Selection The crucial evidence needed for r- and K-selection is whether an organism is allocating a greater proportion of its resources to reproductive activities (r-strategists) than another related one (K .
In summary, r-selection is selection for quantity, K-selection for quality of offspring. Selection for many offspring is most useful in an uncertain, dangerous environment, where most offspring will die anyway, whether the parents invest much resources in their development or not. The more offspring there is, the more chances that at least one . The regulation of population growth by these factors can be used to introduce a classical concept in population biology, that of K-selected versus r-selected species. By the second half of the twentieth century, the concept of K- and r-selected species was used extensively and successfully to study populations. Disturbance is a key factor shaping species abundance and diversity in plant communities. Here, we use a mechanistic model of vegetation diversity to show that different strengths of r- and K-selection result in different disturbance-diversity relationships. R- and K-selection constrain the range of viable species through the colonization-competition tradeoff, .
The r/k selection theory explains whether a species chooses to be a k-strategist or an r-strategist. K-strategists. K-strategists “live” near the carrying capacity k on the population growth curve, under stable environment conditions. They have limited resources. Their population has reached a specific size, and any uncontrolled growth will . For r- and K-selection to occur, there must exist a trade-off between the growth rate at low densities r and γ (or between r and K) because otherwise the evolution of the mean phenotype would always increase the mean growth rate and decrease the mean strength of density regulation resulting in correlated selection for large and K. The regulation of population growth by these factors can be used to introduce a classical concept in population biology, that of K-selected versus r-selected species. K-selected species are species selected by stable, predictable environments. Populations of K-selected species tend to exist close to their carrying capacity (hence the term K .
Overview. In r/K selection theory, selective pressures are hypothesised to drive evolution in one of two generalized directions: r- or K-selection.These terms, r and K, are derived from standard ecological algebra, as illustrated in the simple Verhulst equation of population dynamics: . where r is the growth rate of the population (N), and K is the carrying capacity of its local environmental .
r vs k selection|Difference between r and K Selection
PH0 · r‐ AND K‐SELECTION REVISITED: THE ROLE OF
PH1 · r/K Selection Theory
PH2 · r and K selection
PH3 · What is full form of r and K in r
PH4 · R
PH5 · K and r reproductive strategies
PH6 · K and r Reproductive Strategies
PH7 · ELI5:R/K selection theory, what the hell is it and how does it
PH8 · Difference between r and K Selection